
Nov . 27, 2024 14:53 Back to list
Where to Purchase NPK Ammonium Sulfate Fertilizer for Optimal Plant Growth
The Benefits of Ammonium Sulfate Fertilizer in NPK Nutrition
As the global demand for agricultural production continues to rise, the importance of effective fertilization strategies becomes increasingly critical. Among the myriad of fertilizers available, ammonium sulfate has gained significant attention for its role in enhancing soil fertility and crop yield. This article explores the benefits and application of ammonium sulfate fertilizer within the context of NPK (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium) nutritional requirements in agriculture.
Overview of Ammonium Sulfate
Ammonium sulfate is an inorganic salt with the formula (NH4)2SO4. It is a white crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water, making it easily applicable to a variety of soils. As a source of nitrogen and sulfur, it plays a dual role in plant nutrition, providing essential nutrients that are crucial for crop growth.
Role of Nitrogen in Plant Growth
Nitrogen is one of the three primary macronutrients that plants require, alongside phosphorus and potassium. It is a vital component of amino acids, proteins, and nucleic acids. By supplying nitrogen in the form of ammonium, ammonium sulfate facilitates rapid plant uptake, promoting vegetative growth, chlorophyll synthesis, and overall plant health. This is particularly important for crops that exhibit high nitrogen demand, such as leafy vegetables, cereals, and protein-rich legumes.
The Importance of Sulfur
Sulfur is often overlooked in the discussion of essential nutrients, yet it is crucial for the synthesis of certain amino acids and vitamins. It also plays a key role in enzyme function and photosynthesis. Ammonium sulfate provides sulfur in a readily available form, which can help mitigate deficiencies often observed in high-yield farming practices. Improved sulfur availability leads to enhanced protein content in crops, which is essential for both human and animal nutrition.
NPK Fertilizer Synergy
buy ammonium sulfate fertilizer npk
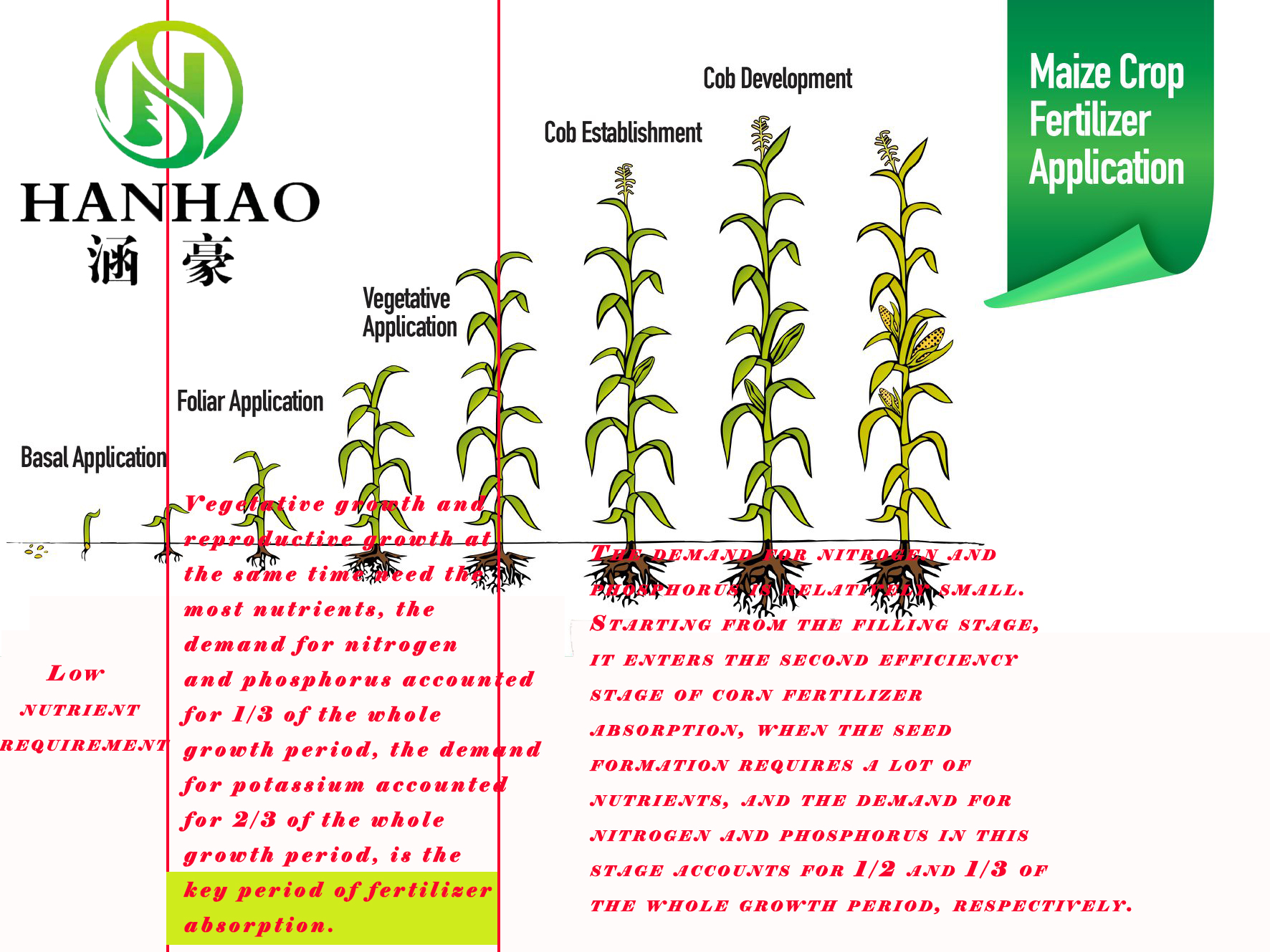
In the context of NPK fertilizers, ammonium sulfate can effectively complement other fertilizers to create a balanced nutritional supply for plants. While nitrogen is supplied by ammonium sulfate, phosphorus and potassium can be added via other fertilizers to achieve an optimal nutrient ratio. This balanced approach ensures that plants receive all the essential nutrients they need to thrive, reducing the risk of nutrient deficiencies and promoting higher crop yields.
Application and Usage
Ammonium sulfate can be applied to soils in several ways, including broadcasting, banding, and incorporation into irrigation systems. The application rate typically depends on soil test results and crop requirements but generally ranges from 50 to 200 kg per hectare. It is essential to apply it at the right time, preferably during the growing season when plants can utilize the nitrogen and sulfur most efficiently.
When using ammonium sulfate, farmers should also consider the overall soil pH, as ammonium can lower pH levels over time. Regular soil testing helps monitor these changes and ensures that necessary adjustments are made to maintain optimal growing conditions.
Environmental Considerations
While ammonium sulfate offers numerous benefits, it is important to use it responsibly to minimize environmental impact. Overapplication can lead to nitrogen leaching and contribute to water quality degradation. Thus, farmers should adopt sustainable practices, such as precision agriculture, to tailor fertilizer applications to specific crop needs and soil conditions.
Conclusion
Ammonium sulfate fertilizer is a vital tool for modern agriculture, particularly in the context of NPK nutrition. Its dual role in providing nitrogen and sulfur makes it an excellent choice for enhancing crop growth and yield. By incorporating ammonium sulfate into balanced fertilization strategies, farmers can meet the nutritional needs of their crops while promoting sustainable farming practices. As the agricultural industry continues to evolve, efficient and responsible use of such fertilizers will be essential in feeding a growing global population while safeguarding the environment.
-
Premium 10 10 10 Fertilizer Organic for Balanced Plant Growth
NewsJul.29,2025
-
Premium 10 10 10 Fertilizer Organic for Balanced Plant Growth
NewsJul.29,2025
-
50 Pound Bags of 13-13-13 Fertilizer for All Plants – Bulk & Organic Options
NewsJul.28,2025
-
High-Efficiency 15-30-15 Granular Fertilizer for Healthy Crops
NewsJul.28,2025
-
15-30-15 Granular Fertilizer for Optimal Crop & Lawn Growth
NewsJul.27,2025
-
Premium 10 10 10 Water Soluble Fertilizer for Fast Plant Growth
NewsJul.26,2025
